Following up my recent post which explains how to find a substring in a string in JavaScript, this post will be dealing with searching for a string or an object in a js array. It’s pretty common to have to search through an array to find a particular string when you’re working with JavaScript. For years the way to search in an array of objects would be to use a for loop to iterate through each item, compare the strings, and then do something when you found a match in the array.
However with the release of ECMAScript 6 in 2015 some new methods were introduced which make searching for a string in an array much easier. In this post we will look at each of these in more detail – Array.includes(), Array.indexOf, Array.find() and you will also be able to find an object in an Array by its property value.
Table of contents
Search for string in JS array – use Array.includes()
Array.includes() is a case sensitive search that will return a true when it finds the first instance of the string or object you’re searching for in the array.
const drinksOrder = ['beer', 'wine', 'coke'];
const doesOrderContainWine = drinksOrder.includes('wine');
console.log(doesOrderContainWine); // true
Search for string in JS array – use Array.indexOf()
Array.indexOf() can be used to find out if an array contains an element, just like Array.includes() above. However it is less readable so personally I use .includes wherever possible. Array.indexOf() also tells us what position the element is in (the first position if there are more than 2 of the same item), so I have included examples of both here.
const drinksOrder = ["beer", "coke", "wine"];
const doesOrderContainWine = drinksOrder.indexOf("wine") >= 0;
const position = drinksOrder.indexOf("wine");
console.log(doesOrderContainWine); // true
console.log("Position of wine in the order :" + position); //2
Search for object in JS array – use Array.find()
Array.find() is described like this in the official documentation:
The
https://developer.mozilla.org/find()method returns the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function. If no values satisfy the testing function,undefinedis returned.
It is especially useful if you’re trying to find an object in an Array by the value of one of its properties, and it can be used in different ways by providing a different testing function. In this example we want to find an object by it’s name property:
const farmAnimals = [
{ name: "horse", quantity: 3 },
{ name: "cat", quantity: 1 },
{ name: "cow", quantity: 15 },
];
let theCat = farmAnimals.find((animal) => animal.name === "cat");
let theChicken = farmAnimals.find((animal) => animal.name === "chicken");
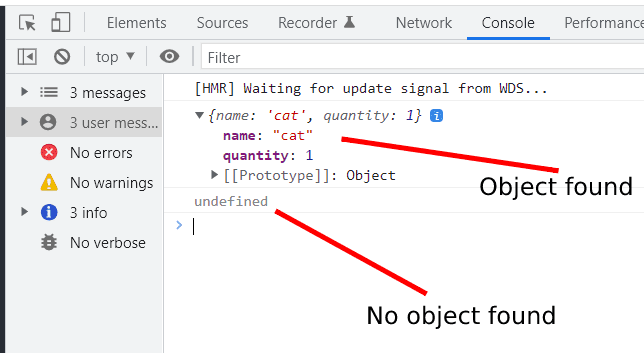
console.log(theCat); //returns the first found object
console.log(theChicken); //returns undefined, as not found
As you can see from the image below if Array.find does find a match then it returns the object it found. If it does not find a match then it returns undefined.
Summary
So that covers it, you should now know how to find a string in a js array of objects, or how to find an object in a Javascript array.
